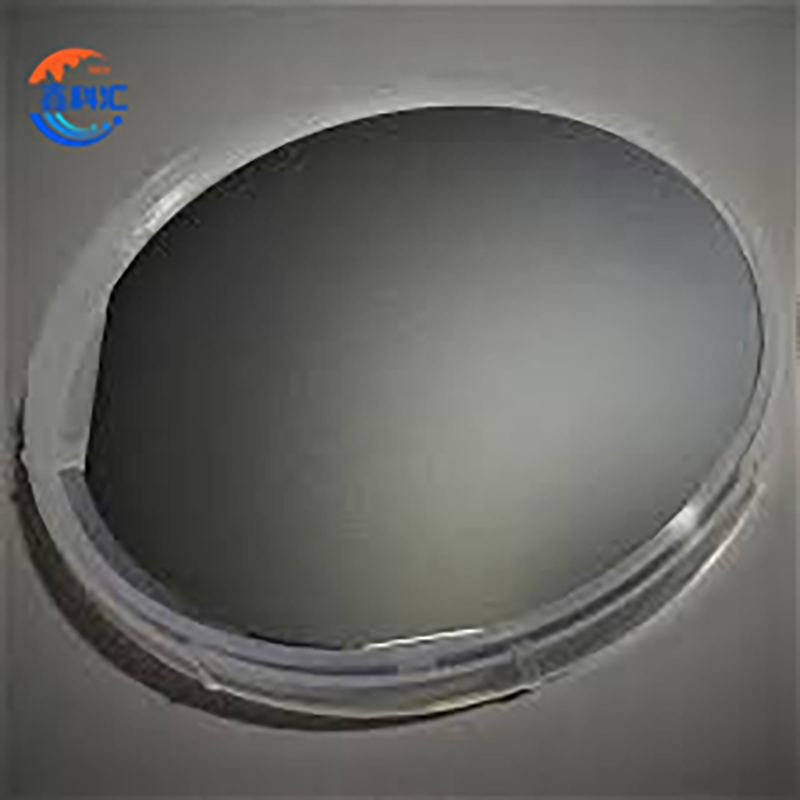
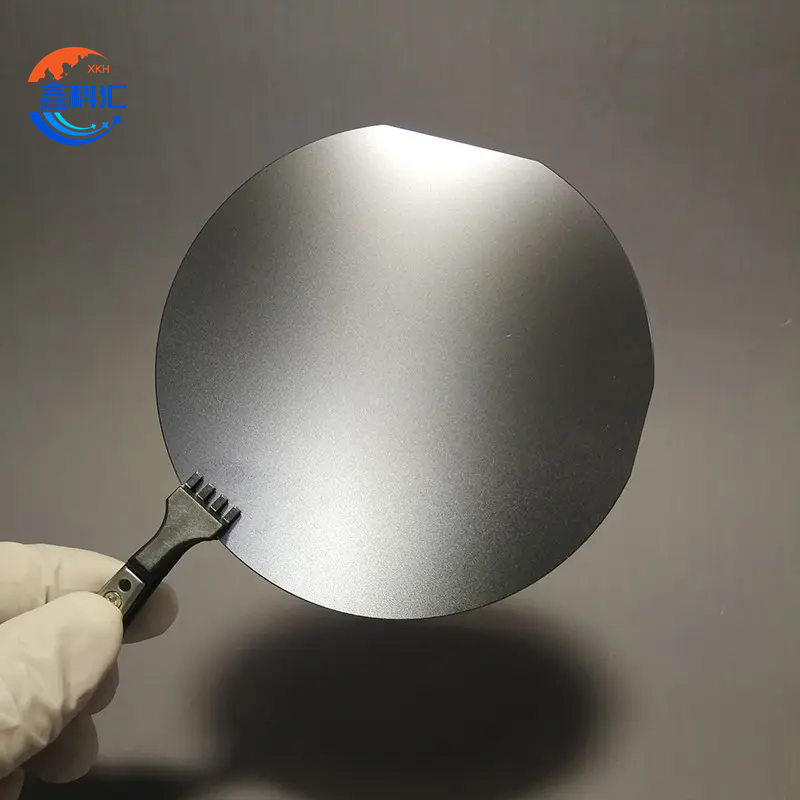
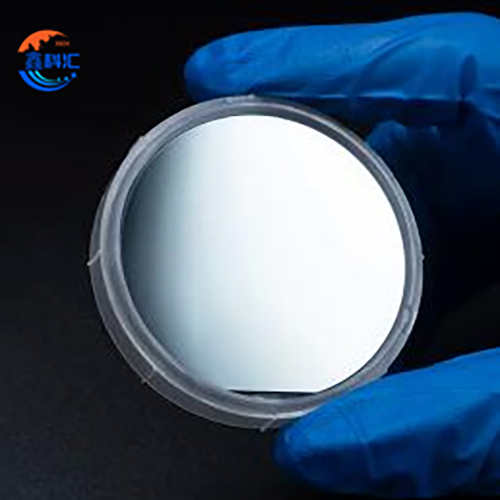
InSb wafer 2inch 3inch undoped Ntype P type orientation 111 100 for Infrared Detectors
Features
Doping Options:
1.Undoped: These wafers are free from any doping agents and are primarily used for specialized applications such as epitaxial growth, where the wafer acts as a pure substrate.
2.N-Type (Te Doped): Tellurium (Te) doping is used to create N-type wafers, offering high electron mobility and making them suitable for infrared detectors, high-speed electronics, and other applications that require efficient electron flow.
3.P-Type (Ge Doped): Germanium (Ge) doping is used to create P-type wafers, providing high hole mobility and offering excellent performance for infrared sensors and photodetectors.
Size Options:
1.The wafers are available in 2-inch and 3-inch diameters. This ensures compatibility with various semiconductor fabrication processes and devices.
2.The 2-inch wafer has a 50.8±0.3mm diameter, while the 3-inch wafer has a 76.2±0.3mm diameter.
Orientation:
1.The wafers are available with orientations of 100 and 111. The 100 orientation is ideal for high-speed electronics and infrared detectors, while the 111 orientation is frequently used for devices requiring specific electrical or optical properties.
Surface Quality:
1.These wafers come with polished/etched surfaces for excellent quality, enabling optimal performance in applications requiring precise optical or electrical characteristics.
2.The surface preparation ensures low defect density, making these wafers ideal for infrared detection applications where performance consistency is critical.
Epi-Ready:
1.These wafers are epi-ready, making them suitable for applications involving epitaxial growth where additional layers of material will be deposited on the wafer for advanced semiconductor or optoelectronic device fabrication.
Applications
1.Infrared Detectors: InSb wafers are widely used in the fabrication of infrared detectors, particularly in mid-wavelength infrared (MWIR) ranges. They are essential for night vision systems, thermal imaging, and military applications.
2.Infrared Imaging Systems: The high sensitivity of InSb wafers allows for precise infrared imaging in various sectors, including security, surveillance, and scientific research.
3.High-Speed Electronics: Due to their high electron mobility, these wafers are used in advanced electronic devices such as high-speed transistors and optoelectronic devices.
4.Quantum Well Devices: InSb wafers are ideal for quantum well applications in lasers, detectors, and other optoelectronic systems.
Product Parameters
|
Parameter |
2-inch |
3-inch |
| Diameter | 50.8±0.3mm | 76.2±0.3mm |
| Thickness | 500±5μm | 650±5μm |
| Surface | Polished/Etched | Polished/Etched |
| Doping Type | Undoped, Te-doped (N), Ge-doped (P) | Undoped, Te-doped (N), Ge-doped (P) |
| Orientation | 100, 111 | 100, 111 |
| Package | Single | Single |
| Epi-Ready | Yes | Yes |
Electrical Parameters for Te Doped (N-Type):
- Mobility: 2000-5000 cm²/V·s
- Resistivity: (1-1000) Ω·cm
- EPD (Defect Density): ≤2000 defects/cm²
Electrical Parameters for Ge Doped (P-Type):
- Mobility: 4000-8000 cm²/V·s
- Resistivity: (0.5-5) Ω·cm
EPD (Defect Density): ≤2000 defects/cm²
Q&A (Frequently Asked Questions)
Q1: What is the ideal doping type for infrared detection applications?
A1: Te-doped (N-type) wafers are typically the ideal choice for infrared detection applications, as they offer high electron mobility and excellent performance in mid-wavelength infrared (MWIR) detectors and imaging systems.
Q2: Can I use these wafers for high-speed electronic applications?
A2: Yes, InSb wafers, particularly those with N-type doping and the 100 orientation, are well-suited for high-speed electronics such as transistors, quantum well devices, and optoelectronic components due to their high electron mobility.
Q3: What are the differences between the 100 and 111 orientations for InSb wafers?
A3: The 100 orientation is commonly used for devices requiring high-speed electronic performance, while the 111 orientation is often used for specific applications that require different electrical or optical characteristics, including certain optoelectronic devices and sensors.
Q4: What is the significance of the Epi-Ready feature for InSb wafers?
A4: The Epi-Ready feature means that the wafer has been pre-treated for epitaxial deposition processes. This is crucial for applications that require the growth of additional layers of material on top of the wafer, such as in the production of advanced semiconductor or optoelectronic devices.
Q5: What are the typical applications of InSb wafers in the infrared technology field?
A5: InSb wafers are primarily used in infrared detection, thermal imaging, night vision systems, and other infrared sensing technologies. Their high sensitivity and low noise make them ideal for mid-wavelength infrared (MWIR) detectors.
Q6: How does the thickness of the wafer affect its performance?
A6: The thickness of the wafer plays a critical role in its mechanical stability and electrical characteristics. Thinner wafers are often used in more sensitive applications where precise control over material properties is required, while thicker wafers provide enhanced durability for certain industrial applications.
Q7: How do I choose the appropriate wafer size for my application?
A7: The appropriate wafer size depends on the specific device or system being designed. Smaller wafers (2-inch) are often used for research and smaller-scale applications, while larger wafers (3-inch) are typically used for mass production and larger devices requiring more material.
Conclusion
InSb wafers in 2-inch and 3-inch sizes, with undoped, N-type, and P-type variations, are highly valuable in semiconductor and optoelectronic applications, particularly in infrared detection systems. The 100 and 111 orientations provide flexibility for various technological needs, from high-speed electronics to infrared imaging systems. With their exceptional electron mobility, low noise, and precise surface quality, these wafers are ideal for mid-wavelength infrared detectors and other high-performance applications.
Detailed Diagram